Nutritional Composition of American Cheese
American cheese nutrition facts label – American cheese, a staple in many households, offers a convenient and familiar source of protein and fat. Understanding its nutritional profile allows for informed choices within a balanced diet. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the macronutrients and micronutrients found in a typical serving, highlighting the balance of fats and their impact on overall health.
Macronutrient Composition of American Cheese
American cheese is primarily composed of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. The exact proportions vary slightly depending on the brand and specific recipe, but a general overview provides a helpful understanding. A typical one-ounce serving contains approximately 8 grams of fat, 7 grams of protein, and 1 gram of carbohydrate. This translates to roughly 110-120 calories per serving.
The percentage of daily value for these macronutrients will depend on individual dietary needs and recommended daily intakes. For example, the fat content contributes significantly to the daily recommended intake, while the protein provides a moderate contribution. The carbohydrate content is minimal.
Micronutrient Content of American Cheese, American cheese nutrition facts label
Beyond the macronutrients, American cheese also provides small amounts of essential micronutrients. These include vitamins like vitamin A, riboflavin (vitamin B2), and calcium. The quantities are relatively modest, and American cheese shouldn’t be considered a primary source of these nutrients. However, the contributions add to the overall nutritional profile of a diet. Precise values will vary based on the cheese’s manufacturing process and ingredients.
Fat Composition in American Cheese
American cheese contains both saturated and unsaturated fats. Saturated fats are generally considered less healthy in excess, while unsaturated fats are deemed more beneficial for cardiovascular health. The ratio of saturated to unsaturated fats in American cheese tends to favor saturated fats. This is important to consider as part of a balanced diet that limits saturated fat intake. The exact proportions vary depending on the type of milk used and the manufacturing process.
Understanding the nutritional content of American cheese, as detailed on its label, is crucial for balanced eating. For those seeking lower-fat alternatives, exploring options like low fat cottage cheese nutrition can be beneficial. Returning to American cheese, careful comparison of its label with other cheeses helps make informed choices about dietary fat intake.
For example, some brands might use milk with a higher fat content, resulting in a higher percentage of saturated fat in the final product.
Nutritional Information Table
| Nutrient | Amount per Serving (1 oz) | % Daily Value (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 110-120 | – |
| Total Fat | 8g | 10-12% |
| Saturated Fat | 5g | 25-30% |
| Cholesterol | 20mg | 7% |
| Sodium | 170mg | 7% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 1g | <1% |
| Protein | 7g | 14% |
| Calcium | 10% | 10% |
| Vitamin A | 6% | 6% |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | 5% | 5% |
Note
Percentage Daily Values are approximate and based on a 2000-calorie diet. Actual values may vary depending on the brand and specific product.
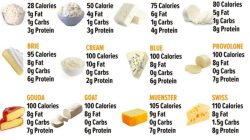
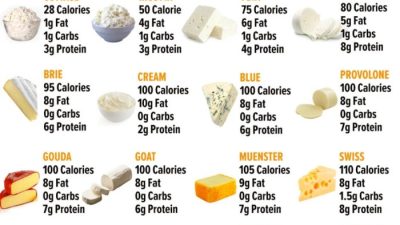
Comparison with Other Cheese Types

American cheese, while a staple in many households, occupies a unique niche in the vast world of cheeses. Understanding its nutritional profile relative to other popular varieties helps consumers make informed choices aligned with their dietary needs and preferences. This section will delve into a comparative analysis of American cheese against cheddar, mozzarella, and Swiss cheese, focusing on key nutritional differences.
The nutritional composition of cheese varies significantly depending on the type, the manufacturing process, and even the specific brand. While general trends exist, individual products can show considerable variation. For example, the fat content in American cheese can fluctuate based on the milkfat percentage used during production, while the sodium content is often influenced by the addition of salt during processing.
This variability underscores the importance of checking the nutritional information label on each specific product.
Nutritional Comparison of American, Cheddar, Mozzarella, and Swiss Cheese
The following table presents a simplified comparison of the approximate nutritional values per 1 ounce serving of American, Cheddar, Mozzarella, and Swiss cheeses. Note that these values are averages and can vary depending on the brand and specific product. Always refer to the individual product’s nutrition label for the most accurate information.
| Cheese Type | Fat (g) | Protein (g) | Sodium (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| American | 8-10 | 7-8 | 170-200 |
| Cheddar | 9-11 | 7-8 | 150-180 |
| Mozzarella | 7-9 | 6-7 | 140-160 |
| Swiss | 8-10 | 7-8 | 100-120 |
This data reveals some key differences. While the protein content remains relatively consistent across these cheese types, the fat content shows minor variations, with Cheddar generally having slightly more fat than the others. A more significant difference lies in the sodium content; American cheese often exhibits higher sodium levels compared to Cheddar, Mozzarella, and particularly Swiss cheese.
Variations in Nutritional Content Among American Cheese Brands
Even within the category of American cheese, considerable variations in nutritional composition can exist between different brands. Factors such as the type of milk used, the processing methods, and the addition of ingredients (like emulsifiers or preservatives) all contribute to these differences. For instance, some brands might opt for a higher milkfat percentage, leading to a higher fat content, while others might prioritize reduced sodium options, resulting in a lower sodium count.
Careful examination of the nutrition facts panel on individual products is crucial for making informed choices based on personal dietary needs and preferences.
For example, Brand A’s American cheese might contain 9g of fat and 180mg of sodium per serving, while Brand B’s might have 7g of fat and 150mg of sodium. These seemingly small differences can accumulate over time and significantly impact overall dietary intake.
Sodium Content and Health Implications

American cheese, a staple in many households, presents a delicious convenience. However, understanding its sodium content and its potential impact on health is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section delves into the sodium content of American cheese, its role in the body, and strategies for managing its consumption.American cheese typically contains a significant amount of sodium per serving.
The exact amount varies depending on the brand and specific product, but a common range is between 200 and 300 milligrams per ounce. This can represent a substantial portion of the recommended daily sodium intake, which is generally set at less than 2,300 milligrams for most adults. This high sodium content warrants careful consideration, especially for certain individuals.
Sodium’s Role in the Body and Blood Pressure
Sodium is an essential electrolyte playing a vital role in maintaining fluid balance, nerve impulse transmission, and muscle contraction. However, excessive sodium intake can lead to increased fluid retention, causing the blood volume to rise. This elevated blood volume forces the heart to work harder to pump blood, resulting in increased blood pressure. This mechanism is particularly relevant for individuals with hypertension or those sensitive to sodium’s effects.
A simple analogy would be a water balloon – as more water (sodium and fluid) is added, the pressure inside increases.
Health Risks Associated with High Sodium Intake from Cheese
High sodium intake, often associated with regular consumption of high-sodium foods like certain cheeses, poses several health risks. Prolonged high blood pressure, a direct consequence of excess sodium, significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke and heart failure. Kidney damage is another potential consequence, as the kidneys work harder to excrete excess sodium. Furthermore, high sodium intake is linked to an increased risk of stomach cancer in some studies.
Reducing Sodium Intake When Using American Cheese
Moderation is key when incorporating American cheese into a balanced diet. Limiting portion sizes is a simple and effective approach. For instance, instead of using two slices on a sandwich, consider using one. Choosing lower-sodium varieties of American cheese, if available, can also contribute to a reduction in overall sodium intake. Balancing the cheese with sodium-rich foods in the diet is important.
For example, if you are having a high sodium meal, you might choose to leave out the cheese. Finally, incorporating a variety of foods rich in potassium, such as bananas and spinach, can help counteract the effects of sodium on blood pressure. These potassium-rich foods help balance the sodium levels in the body.
FAQ: American Cheese Nutrition Facts Label
Is American cheese a good source of protein?
American cheese provides a moderate amount of protein, but its protein content varies depending on the brand and specific type. It’s not considered a primary source of protein compared to lean meats or legumes.
Does American cheese contain any vitamins and minerals?
Yes, American cheese contains small amounts of certain vitamins and minerals, such as calcium and vitamin A, but the quantities are not typically significant enough to contribute substantially to daily requirements.
Can I eat American cheese on a low-fat diet?
While some low-fat versions of American cheese exist, it generally contains a moderate to high amount of fat. Portion control is essential for incorporating it into a low-fat diet.
How does American cheese compare to processed cheese foods?
American cheese and processed cheese foods are often confused. American cheese is a type of processed cheese, but processed cheese foods generally contain additional ingredients like emulsifiers and stabilizers that may alter the nutritional profile.