Nutritional Composition of Swiss Cheese
Swiss cheese nutrition facts – Selamat pagi, semuanya! Let’s dive into the delicious world of Swiss cheese and uncover its nutritional secrets. This creamy, holey delight isn’t just tasty; it packs a punch when it comes to nutrients. We’ll explore its macronutrient profile, vitamin and mineral content, and the types of fats it contains. Prepare to be amazed!
Macronutrient Breakdown of Swiss Cheese
A standard one-ounce serving of Swiss cheese offers a balanced mix of macronutrients crucial for energy and bodily functions. This serving typically contains approximately 80-100 calories, with a significant portion coming from protein and fat. The carbohydrate content is relatively low. Let’s look at a more precise breakdown:Protein: Around 7 grams per ounce. This contributes to building and repairing tissues, and is essential for various bodily processes.
A percentage of daily value (DV) varies depending on individual daily caloric needs, but it’s a decent source.Fat: Approximately 8 grams per ounce. This is where we see a significant portion of the calories. We will explore the types of fat in more detail later.Carbohydrates: Less than 1 gram per ounce. This makes Swiss cheese a suitable option for low-carb diets.
Vitamin and Mineral Content of Swiss Cheese
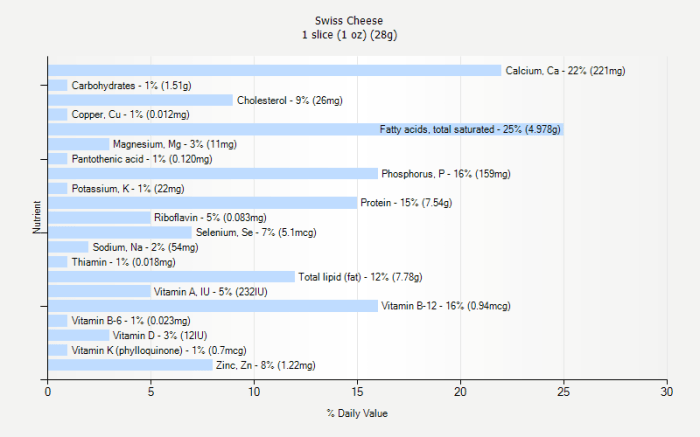
Swiss cheese isn’t just about protein and fat; it’s also a good source of several essential vitamins and minerals. The following table summarizes some key nutrients and their approximate contributions per ounce:
| Nutrient | Amount per ounce (approx.) | % Daily Value (approx.) | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 200mg | 20% | Bone health, muscle function |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | 0.1mg | 8% | Energy metabolism, cell growth |
| Vitamin A | 100 IU | 2% | Vision, immune function |
| Phosphorus | 180mg | 18% | Bone health, energy production |
| Zinc | 1mg | 7% | Immune function, wound healing |
*Note: Daily values can vary based on individual dietary requirements and overall caloric intake. These values are estimates based on average nutritional information.*
Fat Composition and Health Implications of Swiss Cheese
The fat in Swiss cheese is primarily composed of saturated and unsaturated fats. While saturated fats have been historically linked to negative health impacts, moderate consumption as part of a balanced diet is generally considered acceptable. The unsaturated fats in Swiss cheese, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are considered beneficial for heart health when consumed in moderation. It’s important to remember that the overall fat intake should be considered within the context of a person’s overall diet and health goals.
Overconsumption of any type of fat can lead to weight gain and other health issues.
Caloric Content and Serving Sizes: Swiss Cheese Nutrition Facts

Wah, Swiss cheese! So yummy, and surprisingly, it’s got quite a bit going on nutritionally. Let’s dive into the delicious details of its caloric content and how serving size impacts your intake. We’ll make sure to keep it simple and easy to understand, like a good Palembang recipe!
Swiss cheese, with its signature holes and nutty flavor, varies in caloric density depending on the fat content. Generally, one ounce of Swiss cheese contains approximately 100-110 calories. This can fluctuate slightly depending on the brand and the specific type of Swiss cheese. A typical slice might be around 2 ounces, doubling the caloric intake to roughly 200-220 calories.
A cube, depending on its size, could contain anywhere from 50 to 150 calories. Remember, portion control is key to enjoying this delightful cheese without overdoing it!
Discovering the nutritional profile of Swiss cheese, with its delightful nutty flavor, opens a world of healthy possibilities. For a comparison, you might also explore the nutritional details of other cheeses, such as by checking out this helpful resource on monterey jack cheese nutrition , which offers a different taste and texture. Returning to Swiss cheese, remember that mindful cheese consumption, as part of a balanced diet, contributes to overall well-being.
Caloric Comparison of Swiss Cheese with Other Cheeses
Let’s compare the caloric content of Swiss cheese with some other popular choices. This table provides a general overview; actual values may vary slightly depending on the brand and fat content.
| Cheese Type | Calories per Ounce (approx.) |
|---|---|
| Swiss Cheese | 100-110 |
| Cheddar Cheese | 115-125 |
| Mozzarella Cheese | 80-90 |
| Provolone Cheese | 100-110 |
| Parmesan Cheese | 110-120 |
The differences in caloric content primarily stem from variations in fat and water content. For example:
- Higher fat cheeses, like cheddar, generally have more calories per ounce than lower-fat options like mozzarella.
- The water content also plays a role; cheeses with higher moisture content will typically have fewer calories per ounce.
- The type of milk used (whole milk, skim milk, etc.) also impacts the final calorie count.
Visual Representation of Serving Size and Caloric Intake
Imagine a simple bar graph. The horizontal axis represents different serving sizes of Swiss cheese (e.g., 1 ounce, 2 ounces, 3 ounces). The vertical axis represents the total calories. The bars would progressively increase in height as the serving size increases, illustrating the direct relationship between serving size and total caloric intake. For example, a 1-ounce serving might have a short bar, while a 3-ounce serving would have a much taller bar, visually demonstrating the calorie increase with larger portions.
Swiss Cheese in a Balanced Diet

Swiss cheese, with its delightful nutty flavor and characteristic holes, can definitely find a place in a well-rounded diet. Its nutritional profile offers a blend of protein, calcium, and certain vitamins, making it a versatile addition to various meal plans. However, like any food, mindful consumption is key to reaping its benefits without compromising overall health.
Incorporating Swiss cheese into a balanced diet involves understanding its nutritional strengths and weaknesses and adjusting consumption accordingly. Its protein content contributes to satiety and muscle building, while calcium supports bone health. However, its relatively high sodium and fat content requires careful consideration, particularly for individuals with specific dietary restrictions or health concerns.
Nutritional Comparison with Other Dairy Products, Swiss cheese nutrition facts
To better understand Swiss cheese’s place in a dairy-rich diet, let’s compare its nutritional profile with other popular choices. The following table provides a general overview, noting that specific nutritional values can vary depending on the brand and type of cheese.
| Dairy Product | Calories (per ounce) | Fat (per ounce) | Sodium (per ounce) | Calcium (per ounce) | Protein (per ounce) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swiss Cheese | 100-110 | 7-9g | 180-220mg | 200-250mg | 7-8g |
| Cheddar Cheese | 115-125 | 9-11g | 170-200mg | 200-230mg | 7-8g |
| Mozzarella Cheese | 80-90 | 6-8g | 100-150mg | 180-220mg | 6-7g |
| Greek Yogurt (plain) | 70-80 | 3-5g | 50-100mg | 150-200mg | 10-12g |
Note: These values are approximate and can vary depending on the specific product.
Mitigating Dietary Concerns Related to Swiss Cheese
While Swiss cheese offers nutritional benefits, its higher sodium and fat content warrants attention. To mitigate these concerns:
- Portion Control: Sticking to recommended serving sizes helps manage overall sodium and fat intake. A typical serving is about one ounce.
- Balanced Meals: Incorporating Swiss cheese as part of a balanced meal, rather than consuming it alone, can help moderate its impact on the overall nutritional profile of the meal. For example, a sandwich with Swiss cheese, whole-wheat bread, and vegetables provides a more balanced nutritional intake compared to consuming the cheese by itself.
- Dietary Variety: Choosing a variety of dairy products, including lower-fat options like Greek yogurt or part-skim milk, ensures a balanced intake of nutrients without over-relying on any single source of calcium or protein.
- Sodium Awareness: Individuals with hypertension or sodium sensitivity should be particularly mindful of their Swiss cheese consumption and perhaps opt for lower-sodium varieties if available.
Top FAQs
Is Swiss cheese a good source of protein?
Yes, Swiss cheese is a moderate source of protein, contributing to daily protein needs. The exact amount varies depending on serving size and type of Swiss cheese.
Does Swiss cheese contain lactose?
Yes, Swiss cheese contains lactose, although the amount can vary depending on the aging process. Individuals with lactose intolerance may experience varying levels of digestive discomfort.
How does Swiss cheese compare to other cheeses in terms of sodium?
The sodium content of Swiss cheese is moderate compared to some other cheeses, but it’s still advisable to be mindful of intake, especially for individuals with high blood pressure or sodium restrictions.
Can I eat Swiss cheese while on a low-fat diet?
While Swiss cheese contains fat, portion control is key. Choosing smaller servings and incorporating it into a balanced, low-fat diet can be manageable.










